Excessive urination can significantly impact our daily lives, causing inconvenience and discomfort. It's crucial to identify the underlying causes and explore appropriate solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the topic of excessive urination, its common symptoms, and the various factors that contribute to this condition.
Understanding Excessive Urination
Excessive urination, or polyuria, is characterized by the frequent need to urinate and the passing of larger volumes of urine than usual. While the normal frequency of urination varies among individuals, generally, urinating more than 8 times in a 24-hour period or waking up multiple times during the night to urinate can be considered excessive. It's important to note that the specific frequency can vary based on factors such as age, fluid intake, and overall health.
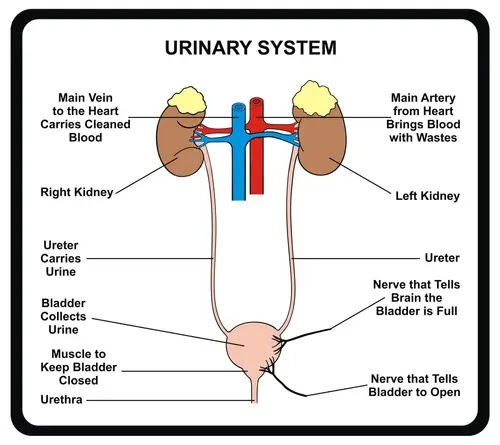 |
| Urinary System |
Common Symptoms Associated with Frequent Urination
- Increased Urge to Urinate: Individuals experiencing excessive urination often have a persistent, urgent need to urinate, which may be difficult to control.
- Nocturia: Nocturia refers to the need to wake up during the night to urinate. This disrupts sleep patterns and can contribute to daytime fatigue.
- Polydipsia: Excessive thirst, known as polydipsia, often accompanies excessive urination. The body tries to compensate for the increased fluid loss by triggering thirst signals.
- Increased Urine Output: Those with excessive urination typically pass larger volumes of urine during each bathroom visit.
- Daytime Frequency: The need to urinate frequently during the day is a common symptom. This can be disruptive to daily activities and may cause inconvenience and discomfort.
Possible Causes of Excessive Urination - The reasons why you peeing so much
1. Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes insipidus is a rare condition characterized by the inability of the body to regulate fluid balance, leading to excessive urine production. Central diabetes insipidus occurs when the body doesn't produce enough antidiuretic hormone (ADH), while nephrogenic diabetes insipidus happens when the kidneys don't respond properly to ADH. Both types result in the kidneys producing large amounts of dilute urine, leading to increased urination. Diabetes insipidus can be caused by damage to the pituitary gland, head trauma, certain medications, or inherited genetic disorders.
2. Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, particularly type 1 and uncontrolled type 2 diabetes, can lead to excessive urination. High blood sugar levels in diabetes cause increased glucose levels in the urine, drawing water into the urine and increasing urine volume. This results in frequent urination as the body attempts to eliminate the excess glucose. Excessive thirst (polydipsia) often accompanies excessive urination in diabetes, as the body tries to compensate for fluid loss. Proper management of blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes is crucial in controlling diabetes-related excessive urination.
3. Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones. These hormones influence various bodily functions, including metabolism and fluid balance. In hyperthyroidism, the increased metabolic rate can lead to an increased filtration rate in the kidneys, resulting in increased urine production and frequency. Other symptoms of hyperthyroidism include weight loss, increased appetite, rapid heartbeat, and nervousness. Treatment options for hyperthyroidism may include medication, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery.
4. Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections of the urinary tract, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), can irritate the bladder and urethra, leading to increased urgency and frequency of urination. UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary system and multiply, causing inflammation and infection. The infection triggers the body's immune response, resulting in increased blood flow to the urinary tract and increased urine production. Common symptoms of UTIs include a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, and a strong urge to urinate. Treatment typically involves antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional.
5. Bladder Infections
Infections specifically targeting the bladder, known as cystitis, can cause inflammation and irritation of the bladder lining. This leads to increased urinary urgency and frequency, as the body tries to flush out the infectious agents. Cystitis is commonly caused by bacterial infection, but it can also result from non-infectious causes such as irritants or autoimmune conditions. Along with increased urination, symptoms may include pelvic pain, discomfort in the lower abdomen, and a persistent need to urinate. Treatment for bladder infections may involve antibiotics, pain relievers, and increased fluid intake to help flush out bacteria.
6. Kidney Infections
Kidney infections, or pyelonephritis, result from bacterial infection in the kidneys. Alongside symptoms like fever and back pain, excessive urination may occur as the body attempts to eliminate the infectious organisms and reduce the inflammatory response. Kidney infections can be serious and require prompt medical attention to prevent complications. Treatment involves antibiotics, pain management, and adequate hydration to support kidney function and flush out bacteria.
7. Prescription Medications That Increase Urine Production
Certain medications, such as diuretics prescribed for conditions like high blood pressure or heart failure, increase urine production. Diuretics work by promoting the excretion of excess fluid and salt from the body, which can result in increased urination. Common types of diuretics include thiazides, loop diuretics, and potassium-sparing diuretics. While these medications can be beneficial for managing certain conditions, they can also contribute to excessive urination. If experiencing bothersome urinary frequency due to medication, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for possible adjustments.
8. Over-the-Counter Diuretics
Over-the-counter diuretics, often used for temporary water weight loss or bloating relief, can increase urine production and result in more frequent urination. These diuretics may contain ingredients like caffeine or herbal extracts known for their diuretic properties. While they may provide short-term relief, prolonged or excessive use of over-the-counter diuretics can disrupt fluid balance and electrolyte levels in the body. It's essential to use these products cautiously and follow the recommended dosage guidelines.
9. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, also known as an enlarged prostate, is a common condition in aging men. The enlarged prostate can obstruct the urethra, interfering with the normal flow of urine. This obstruction causes incomplete bladder emptying, resulting in increased urinary frequency and urgency. Other symptoms of BPH may include weak urine flow, difficulty initiating urination, and the need to strain to empty the bladder. Treatment options for BPH range from medication to surgical procedures, depending on the severity of symptoms and their impact on quality of life.
10. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a malignancy that affects the prostate gland in men. As the tumor grows, it can compress the urethra and interfere with normal urine flow. This can result in increased urinary frequency, urgency, difficulty initiating urination, weak urine stream, or the sensation of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Prostate cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, and prostate biopsy. Treatment options for prostate cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer.
11. Increased Blood Flow to the Kidneys
Conditions that cause increased blood flow to the kidneys, such as congestive heart failure, can result in excessive urine production. Congestive heart failure occurs when the heart fails to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the body. This increased fluid volume stimulates the kidneys to filter more blood, resulting in increased urine production. Consequently, individuals with congestive heart failure may experience frequent urination and increased fluid retention. Proper management of congestive heart failure, including medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications, is crucial to alleviate excessive urination and improve heart function.
12. Pressure on the Bladder
Various factors can exert pressure on the bladder and contribute to frequent urination. For example, in pregnant women, the growing uterus can press against the bladder, leading to increased urinary frequency. Similarly, tumors or growths in the pelvic region can compress the bladder and disrupt normal urinary patterns. Additionally, conditions such as constipation or urinary retention can increase pressure on the bladder and cause the urge to urinate frequently. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause of bladder pressure is essential in managing excessive urination.
13. Muscles in the Bladder Contract Involuntarily
Certain conditions can cause involuntary contractions of the bladder muscles, leading to frequent and urgent urination. Overactive bladder (OAB) is a common condition characterized by sudden, uncontrollable urges to urinate, even when the bladder isn't full. These urges can result in frequent trips to the bathroom, disrupting daily life. OAB can be caused by various factors, including nerve damage, bladder infections, or neurological disorders. Treatment options for OAB may include lifestyle modifications, pelvic floor exercises, medications, or bladder nerve stimulation.
14. Frequent Urgent Need to Urinate
Some individuals experience a frequent and urgent need to urinate without an underlying medical condition. This can be attributed to factors such as excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, increased stress levels, or heightened nervousness or anxiety. Caffeine and alcohol act as diuretics, stimulating the kidneys to produce more urine. Additionally, stress and anxiety can activate the body's "fight-or-flight" response, which can trigger the urge to urinate as a physiological reaction. Managing these contributing factors through moderation of caffeine and alcohol intake, stress reduction techniques, and relaxation exercises may help alleviate the frequent urge to urinate.
15. Chronic Bladder Inflammation
Chronic inflammation of the bladder, known as chronic cystitis, can contribute to increased urination frequency. The persistent inflammation irritates the bladder lining, causing discomfort and the need to empty the bladder more frequently. Chronic cystitis can be caused by recurrent bladder infections, bladder irritants (such as certain foods or medications), or underlying conditions such as interstitial cystitis. Treatment options for chronic cystitis may include lifestyle modifications, medications to reduce inflammation, bladder instillations, or physical therapy techniques to improve bladder function.
16. Increased Urinary Frequency and Urgency
Certain neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) or spinal cord injuries, can disrupt the normal communication between the brain and the bladder. This can result in increased urinary frequency and urgency. Neurological damage affects the nerve signals that control bladder function, leading to involuntary contractions and a reduced ability to hold urine. Management of neurological disorders may involve medication, physical therapy, bladder training techniques, or intermittent catheterization to manage urinary symptoms.
17. Drinking Large Amounts of Fluids, Especially Caffeinated or Alcoholic Beverages
Consuming large quantities of fluids, particularly those containing caffeine or alcohol, can increase urine production and lead to more frequent urination. Caffeine and alcohol are diuretics that promote fluid excretion by the kidneys. As a result, excessive intake of caffeinated or alcoholic beverages can cause fluid imbalance and stimulate the need to urinate frequently. Moderating the consumption of these beverages and maintaining a balanced fluid intake can help regulate urinary frequency.
18. Anxiety
Anxiety can have a significant impact on urinary patterns, leading to increased urination frequency. Anxiety triggers the body's stress response, which releases stress hormones that can affect bladder function. The body's fight-or-flight response can stimulate the bladder and result in frequent urges to urinate, even when the bladder isn't full. Managing anxiety through relaxation techniques, therapy, or medication can help alleviate excessive urination associated with anxiety.
19. Stress
Similar to anxiety, stress can also influence urinary patterns and contribute to increased urination. Stress activates the body's stress response, leading to physiological changes, including increased blood flow to the kidneys and increased urine production. Chronic stress can disrupt the normal balance of the body's systems, including the urinary system, and result in frequent urination. Adopting stress-management techniques, such as exercise, mindfulness, or counseling, can help reduce stress-related excessive urination.
20. Nervousness
Feelings of nervousness or excitement can stimulate the bladder and result in more frequent urination. This response is similar to the body's reaction to anxiety or stress. Taking measures to calm nerves or engaging in relaxation techniques may help alleviate the urge to urinate frequently due to nervousness.
21. Bladder or Kidney Stones
The presence of bladder or kidney stones can irritate the urinary tract, causing increased urination frequency and urgency. Stones can obstruct the flow of urine, resulting in discomfort and altered urinary patterns. Treatment for bladder or kidney stones depends on the size and location of the stones and may involve medication, lifestyle changes, or medical procedures.
22. Neurological Disorders
Neurological conditions that affect the nerves controlling the bladder, such as Parkinson's disease, stroke, or spinal cord injuries, can disrupt the normal coordination of bladder function. This can lead to increased urinary frequency and urgency. Management of neurological disorders may involve a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to address urinary symptoms.
23. Certain Cancers
Certain types of cancer, such as bladder, kidney, or prostate cancer, can cause changes in urination patterns. Tumors can obstruct the urinary tract, leading to increased urgency and frequency. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing cancer-related urinary symptoms. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
24. Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure can cause fluid retention in the body, leading to increased blood volume and increased urine production. The kidneys attempt to remove the excess fluid, resulting in more frequent urination. Management of congestive heart failure involves a comprehensive approach that may include medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications.
Solutions and Management Techniques
Excessive urination can significantly impact daily life, but fortunately, there are several solutions and management techniques available to help address the underlying causes and alleviate symptoms. The following strategies can be implemented to manage excessive urination effectively:
Lifestyle Changes
1. Decrease Fluid Intake Before Bedtime
Limiting fluid intake, especially in the evening hours, can help reduce the frequency of nighttime urination. Drinking smaller amounts of fluid earlier in the day and avoiding excessive fluid consumption close to bedtime can minimize the need to wake up repeatedly during the night to use the bathroom. It is essential to strike a balance between staying hydrated and managing excessive urination.
2. Avoid Bladder Irritants
Certain substances can irritate the bladder and contribute to increased urination frequency. Common bladder irritants include caffeine, alcohol, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, and artificial sweeteners. These substances can stimulate the bladder and increase urine production. By identifying and avoiding these bladder irritants, individuals can help reduce bladder irritation and subsequent excessive urination.
3. Manage Stress and Anxiety Levels
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate urinary symptoms and contribute to increased urination. Implementing stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, regular exercise, and engaging in activities that promote relaxation can help reduce stress-related urinary frequency. Additionally, seeking support from mental health professionals or therapists can provide valuable coping strategies to manage stress and anxiety effectively.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can put pressure on the bladder and contribute to urinary urgency and frequency. Engaging in regular physical activity and adopting a balanced diet can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the strain on the bladder and potentially improving urinary control.
Medical Interventions
1. Medications to Treat Underlying Conditions
If the excessive urination is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes, urinary tract infection (UTI), or prostate enlargement, medications may be prescribed to manage the condition and alleviate urinary symptoms. For example, antidiabetic medications or insulin may be prescribed for diabetes-related excessive urination, while antibiotics are used to treat UTIs. Medications to relax the muscles of the bladder or reduce bladder inflammation may also be prescribed, depending on the underlying cause.
2. Surgical Procedures for Enlarged Prostate or Bladder Issues
In cases where an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or bladder issues are causing excessive urination, surgical interventions may be recommended. Procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), laser surgery, or bladder augmentation can help relieve urinary symptoms and improve bladder function. These procedures aim to alleviate urinary obstruction, reduce urinary urgency, and restore normal urine flow.
3. Treatment of Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in conditions like diabetes insipidus or hyperthyroidism, can contribute to excessive urination. Treating the underlying hormonal imbalance through medication, hormone replacement therapy, or other appropriate interventions can help regulate urine production and reduce urinary frequency.
Behavioral Techniques
1. Bladder Training Exercises
Bladder training involves gradually increasing the time intervals between bathroom visits to help train the bladder to hold urine for longer periods. This technique can be effective in reducing urinary frequency and improving bladder control. The process typically starts with delaying bathroom visits by a few minutes and gradually increasing the intervals over time. Bladder training exercises may also include techniques like double voiding, which involves emptying the bladder twice during each bathroom visit to ensure complete emptying.
2. Scheduled Voiding
Establishing a regular voiding schedule can help regulate urinary patterns and reduce the frequency of excessive urination. Setting specific times for bathroom visits, even if the urge is not present, can help train the bladder and promote more controlled urination. For example, an individual may schedule bathroom visits every two to three hours during the day, gradually increasing the interval as urinary control improves.
3. Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises known as Kegel exercises can help improve bladder control and reduce urinary urgency. These exercises involve contracting and relaxing the muscles that support the bladder and urethra. Regular practice of pelvic floor exercises can enhance muscle tone and increase control over urinary function.
Herbal Remedies and Alternative Therapies
1. Cranberry Supplements for UTIs
Cranberry supplements or products containing cranberry extract can help prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs), which can contribute to increased urination frequency. Cranberries contain compounds that inhibit bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls, reducing the risk of infection. However, it is important to note that cranberry supplements should be used as a preventive measure and should not replace medical treatment for existing UTIs.
2. Acupuncture for Bladder Control
Acupuncture, an alternative therapy that involves the insertion of thin needles at specific points on the body, has been used to manage urinary symptoms, including excessive urination. Acupuncture may help improve bladder control and reduce urinary urgency and frequency in some individuals. It is recommended to seek a qualified and experienced acupuncturist for this therapy.
3. Herbal Diuretics
Certain herbal diuretics, such as dandelion root or parsley, may have diuretic properties and promote increased urine production. However, the use of herbal diuretics should be approached with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It is important to consider individual health conditions and any potential interactions with medications.
You should consult with a healthcare professional or specialist to determine the most appropriate management plan based on the underlying cause of excessive urination and individual circumstances. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, offer personalized recommendations, and monitor the effectiveness of the chosen interventions.









0 Comments