Are you experiencing stomach pain and wondering why it's happening? Stomach pain can disrupt your daily life and leave you searching for answers. Understanding the causes behind this discomfort is crucial in finding appropriate remedies and restoring your well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various reasons why your stomach might hurt and provide valuable insights to help you find relief. Whether it's a result of gastrointestinal infections, indigestion, acid reflux, or other factors, we've got you covered. So, let's explore the mysteries of stomach pain and empower you with the knowledge to overcome it.
 |
| Stomach Pain |
Understanding Stomach Pain
The first step in addressing stomach pain is to gain a clear understanding of what it entails. Stomach pain, also known as abdominal pain, is a broad term that encompasses a range of sensations and discomforts in the abdominal region. It can manifest in different ways, such as cramping, sharp or dull aches, bloating, or a general feeling of unease.
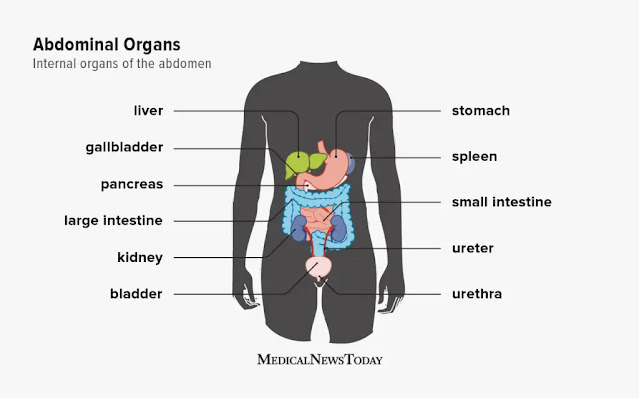 |
| Abdominal Organs |
Identifying the exact location and type of pain is crucial in determining its underlying cause. Stomach pain can originate from various organs within the abdomen, including the stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, appendix, and reproductive organs. By pinpointing the specific location and nature of the pain, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and treat the underlying condition.
To accurately describe your stomach pain, it's helpful to consider factors such as the intensity, duration, and frequency of the pain, as well as any associated symptoms. This information will aid in the diagnostic process and enable healthcare providers to tailor a suitable treatment plan.
By understanding the different manifestations and characteristics of stomach pain, you become an active participant in your own healthcare. It allows you to communicate effectively with medical professionals and seek appropriate solutions for your specific situation. So, let's embark on a journey through the various causes of stomach pain to shed light on this common yet often perplexing issue.
The Reasons Why Your Stomach Hurts
1. Gastrointestinal Infections
Gastrointestinal infections are a common cause of stomach pain and can be caused by various bacteria, viruses, or parasites. These infections often result in symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. It's important to recognize the signs of a gastrointestinal infection and take appropriate measures for treatment and prevention.
 |
| Gastrointestinal Infections |
- Symptoms: Gastrointestinal infections can present with symptoms like frequent watery stools, fever, loss of appetite, and dehydration. In severe cases, bloody stools or persistent vomiting may occur.
- Causes: Gastrointestinal infections can be caused by consuming contaminated food or water, poor hygiene practices, or close contact with infected individuals. Bacteria like Salmonella, Escherichia coli (E. coli), and Campylobacter, as well as viruses like norovirus and rotavirus, are common culprits.
- Treatment and Prevention: Treatment for gastrointestinal infections usually involves rest, hydration to prevent dehydration, and symptomatic relief. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is suspected. Prevention strategies include practicing good hand hygiene, ensuring food safety through proper cooking and storage, and avoiding consuming water or food from questionable sources.
2. Indigestion and Gas
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, and gas can cause discomfort and pain in the stomach. It is often associated with overeating, consuming spicy or fatty foods, eating too quickly, or swallowing excess air while eating or drinking. Understanding the triggers and implementing lifestyle changes can help alleviate these symptoms.
- Common Triggers and Symptoms: Indigestion and gas can manifest as a feeling of fullness, bloating, belching, and abdominal discomfort. Certain foods and beverages, such as carbonated drinks, onions, garlic, and caffeine, can contribute to these symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making certain adjustments to your lifestyle can help manage indigestion and gas. These include eating smaller, more frequent meals; chewing food thoroughly; avoiding trigger foods; refraining from lying down immediately after eating; and reducing stress levels during mealtime.
- Over-the-counter Remedies: Over-the-counter antacids can provide temporary relief from indigestion and gas. Antacids work by neutralizing stomach acid and reducing bloating. It's important to follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
3. Acid Reflux or Heartburn
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, resulting in a burning sensation in the chest known as heartburn. Acid reflux can be caused by certain foods, obesity, smoking, pregnancy, or a weakened lower esophageal sphincter (LES).
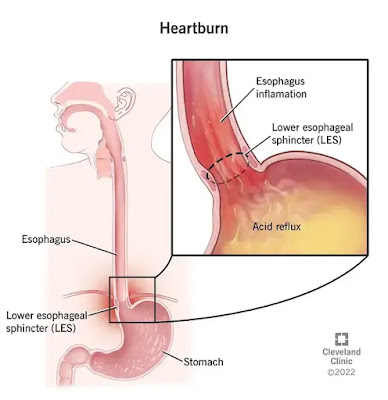 |
| Heartburn |
- Explanation: Acid reflux occurs when the LES, a ring of muscle between the esophagus and the stomach, fails to close properly. This allows stomach acid to enter the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort.
- Causes: Certain foods and beverages, such as spicy foods, citrus fruits, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol, can trigger acid reflux. Other factors, such as obesity, smoking, and certain medications, can weaken the LES and contribute to the development of acid reflux.
- Treatment Options: Treatment for acid reflux involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medications. Lifestyle changes may include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding trigger foods, elevating the head of the bed while sleeping, and quitting smoking. Medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2 blockers, and antacids can help reduce stomach acid production and provide relief. In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to strengthen the LES.
4. Gastritis
Gastritis refers to inflammation of the stomach lining and can be acute or chronic. It can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness. Gastritis can be triggered by various factors, including infection, certain medications, excessive alcohol consumption, and prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
 |
| Gastritis |
- Overview: Gastritis occurs when the protective lining of the stomach becomes inflamed, leading to irritation and discomfort. It can be caused by bacterial infections, such as Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), autoimmune diseases, excessive stomach acid production, or prolonged use of NSAIDs.
- Possible Causes: Infection with H. pylori is a common cause of gastritis. This bacterium can lead to chronic inflammation of the stomach lining. Gastritis can also be caused by excessive alcohol consumption, regular use of NSAIDs (such as aspirin or ibuprofen), and certain autoimmune diseases, such as pernicious anemia.
- Treatment Methods: Treatment for gastritis aims to alleviate symptoms, promote healing of the stomach lining, and address the underlying cause. Depending on the cause, treatment may involve antibiotics to eradicate H. pylori, medications to reduce stomach acid production, lifestyle modifications (such as avoiding trigger foods and alcohol), and discontinuing the use of NSAIDs.
5. Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach or the upper part of the small intestine. They can cause stomach pain, bloating, heartburn, and in some cases, bleeding. The primary causes of peptic ulcers include infection with H. pylori bacteria and the use of NSAIDs.
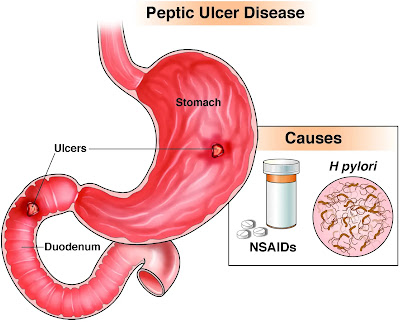 |
| Peptic Ulcers |
Explanation: Peptic ulcers occur when there is an imbalance between the protective factors and the damaging factors that affect the stomach lining. The acidic digestive juices, combined with H. pylori infection or the use of NSAIDs, can erode the protective layer, leading to ulcer formation.
Causes: The most common cause of peptic ulcers is infection with H. pylori bacteria. These bacteria weaken the protective lining of the stomach, making it susceptible to damage from stomach acid. Regular use of NSAIDs, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, can also contribute to peptic ulcers by irritating the stomach lining.
Treatment Options: Treatment for peptic ulcers involves a combination of antibiotics to eradicate H. pylori infection, medications to reduce stomach acid production, and lifestyle modifications. In some cases, endoscopic procedures may be necessary to stop bleeding or to repair the ulcer.
6. Food Allergies or Intolerances
Food allergies or intolerances can cause stomach pain and digestive discomfort. These conditions occur when the immune system reacts to specific proteins in food or when the body has difficulty digesting certain substances. Common food allergens include peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, eggs, milk, wheat, and soy.
 |
| Food Allergies and Intolerances |
- Discussion of Common Food Allergies and Intolerances: Food allergies involve an immune response to certain foods, triggering symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, hives, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis. Food intolerances, on the other hand, occur when the body lacks certain enzymes necessary for digesting specific substances, leading to digestive symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Symptoms and How They Relate to Stomach Pain: Food allergies and intolerances can manifest with various gastrointestinal symptoms, including stomach pain. These symptoms can occur shortly after consuming the triggering food and may be accompanied by other signs like skin rashes, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Management Strategies: Managing food allergies and intolerances involves identifying and avoiding trigger foods. This may require keeping a food diary, undergoing allergy testing, and working with a healthcare professional or dietitian to develop an appropriate meal plan. In some cases, medical guidance and the use of medication may be necessary to manage severe allergic reactions.
7. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine. It is characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, changes in bowel habits (such as diarrhea or constipation), and an overall impact on quality of life.
 |
| Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) |
Overview: IBS is a chronic condition that affects the function of the large intestine. While the exact cause is unknown, factors such as abnormal muscle contractions in the intestine, hypersensitivity to certain foods, stress, and changes in gut bacteria have been implicated.
Common Symptoms: Abdominal pain or discomfort is a hallmark symptom of IBS. Other symptoms include bloating, gas, changes in bowel movements (ranging from diarrhea to constipation or alternating between the two), and a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying.
Lifestyle Modifications and Medical Interventions: Managing IBS involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Dietary changes, such as following a low-FODMAP diet (which restricts certain fermentable carbohydrates), stress management techniques, regular exercise, and probiotic supplements, may help alleviate symptoms. In more severe cases, medication prescribed by a healthcare professional may be necessary to control symptoms.
8. Gallstones
Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ responsible for storing bile. They can cause stomach pain, especially after consuming fatty or greasy foods, and may require medical intervention for removal.
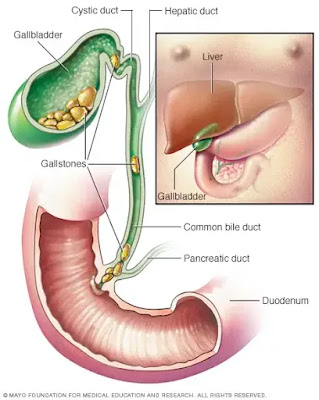 |
| Gallstones |
Explanation: Gallstones can form when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, such as cholesterol and bilirubin. These substances can crystallize and form stones in the gallbladder.
Risk Factors and Symptoms: Risk factors for developing gallstones include being female, overweight or obese, having a family history of gallstones, and rapid weight loss. The most common symptom of gallstones is sudden, intense pain in the upper right abdomen, known as biliary colic. This pain can radiate to the back or shoulder.
Treatment Options: Treatment for gallstones may involve medication to dissolve the stones, but surgery, such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is often necessary for complete removal of the gallbladder. This procedure is commonly performed and does not affect digestion significantly.
9. Appendicitis
Appendicitis refers to inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine. It is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate surgical removal of the inflamed appendix.
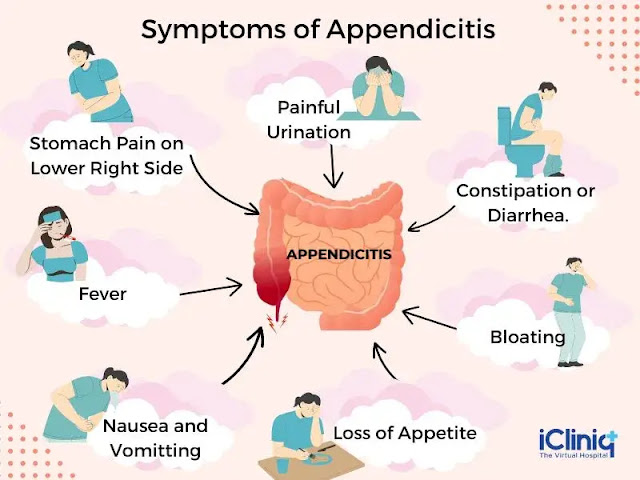 |
| Appendicitis |
Brief Explanation: Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, often due to the buildup of hardened stool, enlarged lymphoid tissue, or, in rare cases, tumors. The blockage can lead to bacterial overgrowth and inflammation.
The Urgency of Seeking Medical Attention: Appendicitis typically presents with severe abdominal pain that starts around the navel and migrates to the lower right abdomen. Other symptoms may include fever, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. If left untreated, a ruptured appendix can lead to serious complications like peritonitis, a potentially life-threatening infection.
Surgical Removal of the Appendix: The primary treatment for appendicitis is an appendectomy, which involves the surgical removal of the inflamed appendix. This procedure is usually performed using laparoscopic techniques, resulting in faster recovery times and minimal scarring.
10. Menstrual Cramps
Menstrual cramps, also known as dysmenorrhea, are a common cause of lower abdominal pain experienced by many menstruating individuals. They occur due to the contraction of the uterine muscles during menstruation.
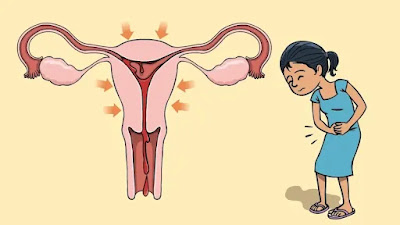 |
| Menstrual Cramps |
a. Connection Between Menstrual Cramps and Stomach Pain: Menstrual cramps can cause pain in the lower abdomen that may be perceived as stomach pain. The contractions of the uterus can also affect the neighboring digestive organs, leading to bloating and discomfort.
b. Tips for Managing Menstrual Pain: Various strategies can help manage menstrual cramps and alleviate stomach pain. These include applying heat to the abdomen, taking over-the-counter pain relievers, practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in light physical activity, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle overall.
How to Relieve Stomach Pain
1. Dietary Changes
- Foods to Avoid and Foods That May Help Alleviate Stomach Pain: Certain foods can trigger or exacerbate stomach pain, such as spicy and fatty foods, carbonated drinks, and caffeine. On the other hand, incorporating a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and probiotic-rich foods may help alleviate stomach pain and promote digestive health.
- Importance of Maintaining a Balanced Diet: A balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients for optimal digestive function and overall well-being. It's crucial to include a variety of foods from different food groups to ensure adequate nutrient intake and support a healthy digestive system.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Stress can contribute to stomach pain and digestive issues. Implementing stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, regular physical activity, and getting sufficient sleep can help improve overall digestion and reduce stomach pain.
- Regular Exercise and Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise can help promote healthy digestion by stimulating bowel movements and reducing constipation. It also aids in weight management, which can alleviate pressure on the stomach and reduce the risk of certain digestive disorders.
3. Over-the-counter Medications
- Commonly Used Medications for Stomach Pain Relief: Over-the-counter medications like antacids, which neutralize stomach acid, and anti-diarrheal medications, which help alleviate diarrhea symptoms, can provide temporary relief from stomach pain. It's important to follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
- Dosage Instructions and Potential Side Effects: When using over-the-counter medications, it's crucial to carefully read and follow the dosage instructions provided. Some medications may have potential side effects or interactions with other medications, so it's important to consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
4. Home Remedies
- Natural Remedies for Stomach Pain Relief: Several natural remedies may help alleviate stomach pain. These include herbal teas, such as peppermint or chamomile, which have soothing properties, and essential oils like ginger or fennel oil, which can aid digestion when used in moderation. It's important to use these remedies cautiously and consult a healthcare professional if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
- Herbal Teas, Essential Oils, and Other Alternative Approaches: Herbal teas can help relax the stomach muscles and reduce inflammation, while essential oils can be used topically or aromatically to provide relief. However, it's essential to ensure the quality and purity of the herbal teas and essential oils used, as well as to be mindful of any potential allergies or sensitivities.
👉 Read more posts with the same topic
Conclusion
Stomach pain can stem from various causes, including gastrointestinal infections, indigestion and gas, acid reflux, gastritis, peptic ulcers, food allergies or intolerances, irritable bowel syndrome, gallstones, appendicitis, and menstrual cramps.
Identifying the underlying cause of stomach pain is crucial for effective management and treatment. It may require medical evaluation, diagnostic tests, and consultation with a healthcare professional to accurately diagnose and address the specific cause.Strategies for managing and relieving stomach pain include dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter medications, and home remedies. It's important to adopt a comprehensive approach that addresses the root cause and promotes overall digestive health.
If stomach pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis, develop an appropriate treatment plan, and offer guidance for managing stomach pain effectively.








0 Comments